| Design Engineering Theory Topics - Home Page |
Using communication techniques to present design ideas
1 - Freehand sketching
- Freehand sketches are drawings that are created using no technical equipment such as T squares, set squares and rulers.
- Allows to show ideas in 3D and/or 2D.

To make it more effective:
- different media, i.e. using pencils, ball point pens, fine liners, marker pens or coloured pencils.
- grid paper can be helpful in showing scale or added a human figure.
- use of arrows is a good way to show movement in certain directions.
2 - Digital photography / media
- Ideas are created by editing photos and media.
- Can be as simple as tracing over the top of an existing photograph.
- Often used in making billboard advertising for new films.
3 - Cut and paste techniques
- Used by fashion designers to use existing photos/images to help and inspire their own designs.
- Again can be achieved by using tracing paper over an existing photo.
4 - 3D models
- To help the user visual the end product prototypes or 3D models are sometimes made.
- can be full size or smaller scale
- can be made from a variety of materials - paper, fabric, cardboard, stryofoam or HIPS.
- can be made from small plastic building bricks
- system modelling can use breadboards or stripboard
- computer modelling to make 3D printed models and simulations.




5 - 3D drawing
Can be isometric, oblique, one point perspective or two-point perspective.
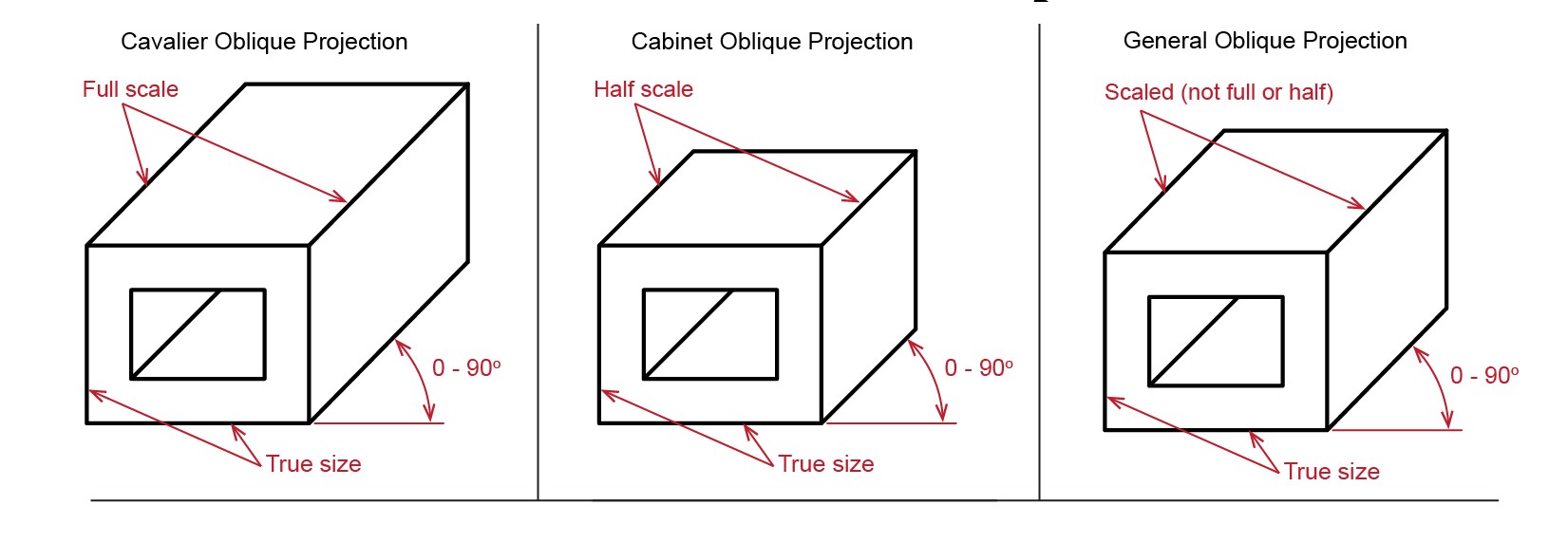
Oblique and isometric projections
Isometric projections
Oblique projections
- 45 degrees is the angle for all lines drawn backwards.
One point perspective drawing
- Often used in interior design.
- Construction lines point in the distance to a single point called the vanishing point.

Two point perspective drawing
- Two-point perspective uses two vanishing points, connected by a horizontal line.
- Two-point perspective is useful when developing ideas in 3D.

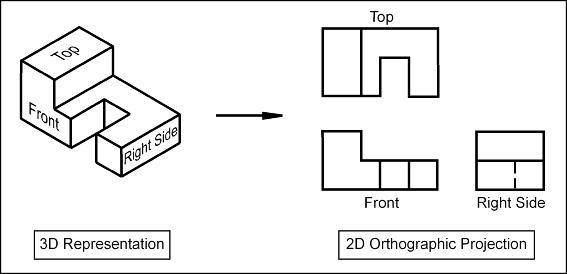
Orthographic and exploded views
- Orthographic projection uses a 2D drawing of each side of an object.
- Orthographic drawings usually consist of a front view, a side view and a plan view.
- A drawing board and parallel motion or T-square is used to project one view from another.
- Orthographic drawing may be done using first angle projection or third angle projection.
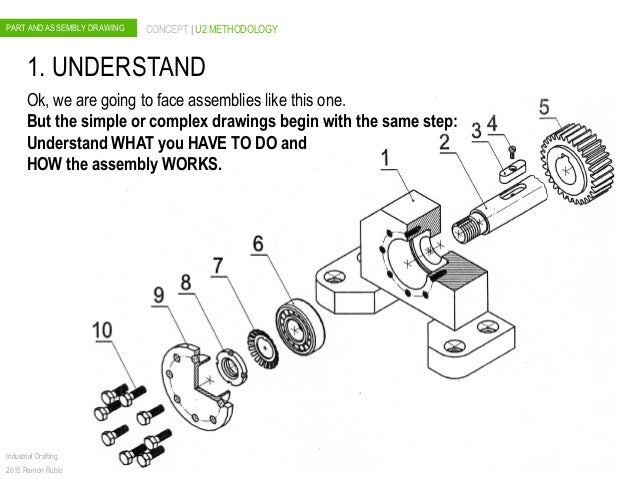
Exploded view
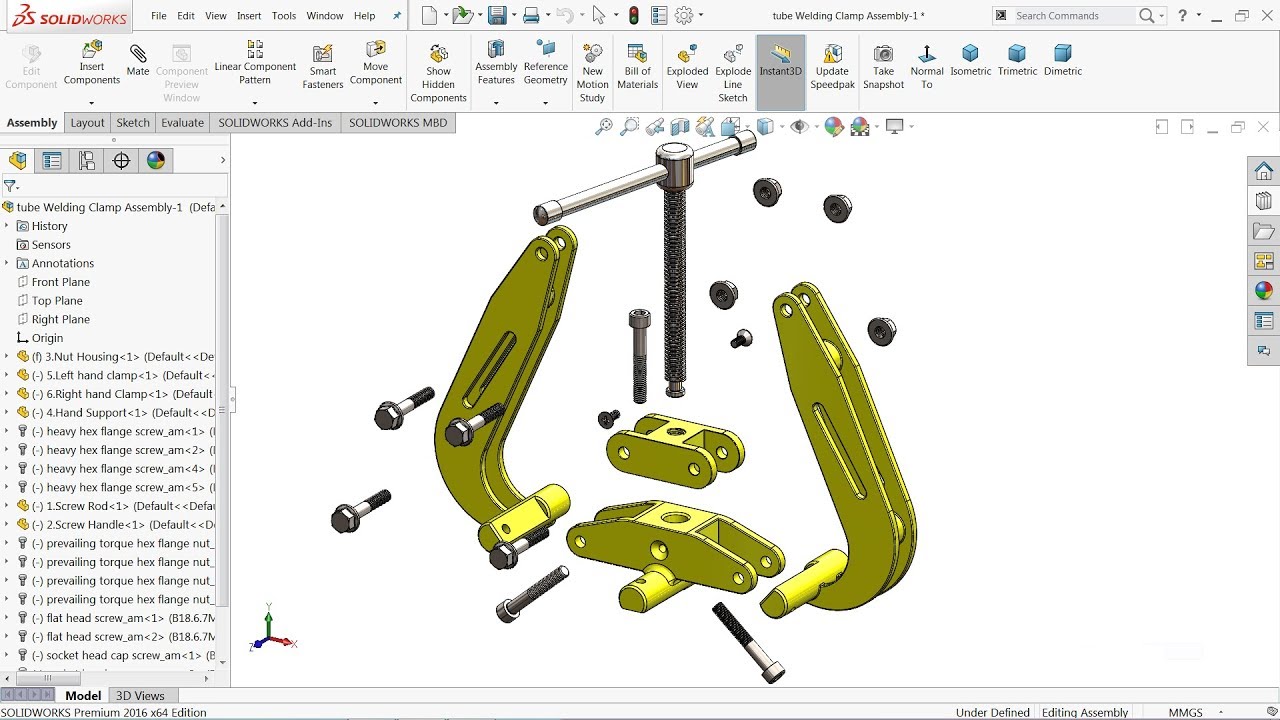
Assembly drawings
- An assembly drawing shows how parts of a product fit together.
- They are often used to show how to assemble parts of model kits and flat-pack furniture.
- There are two types:
- A fitted assembly drawing shows the parts put together, and can be drawn in 2D or 3D.
- An exploded drawing shows the parts separated, but in the correct relationship for fitting together. Exploded views are usually drawn in 3D, as illustrated.
6 Systems and schematic diagrams
- used mainly for electronic projects
- shows the inputs, processes and outputs
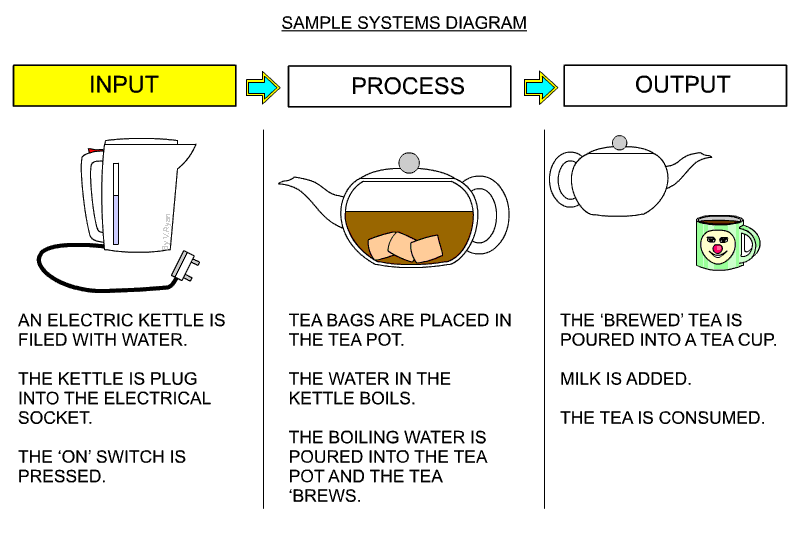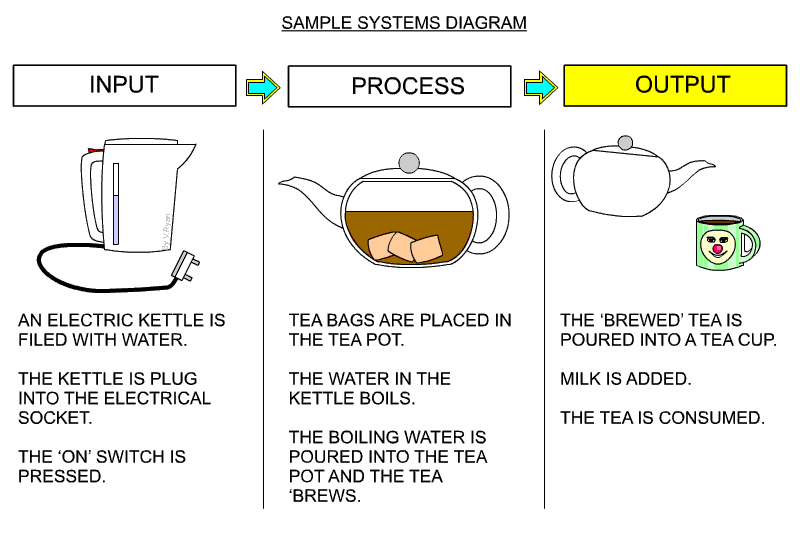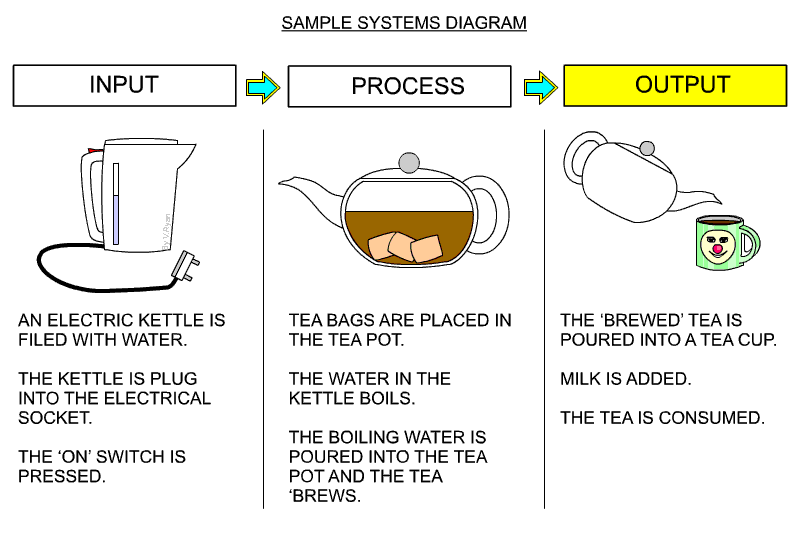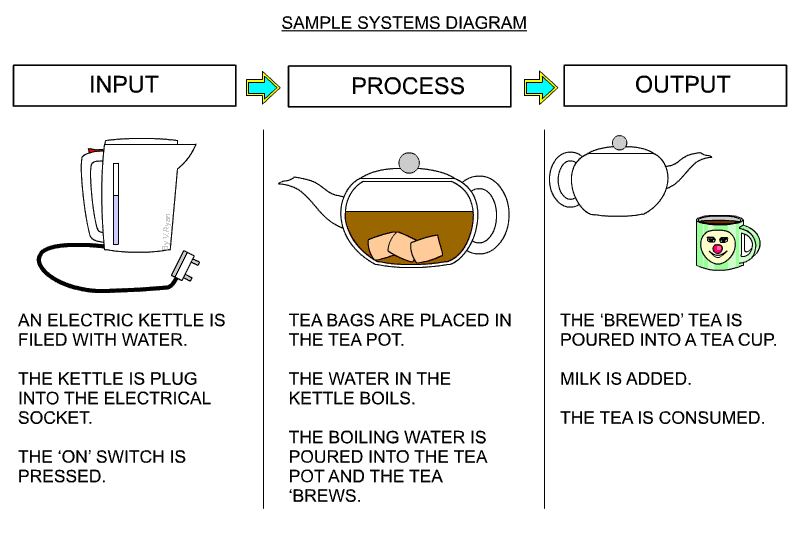
Schematic
- maybe hand drawn or made using a computer package such as Circuit Wizard.
- labelled to show component names and values.
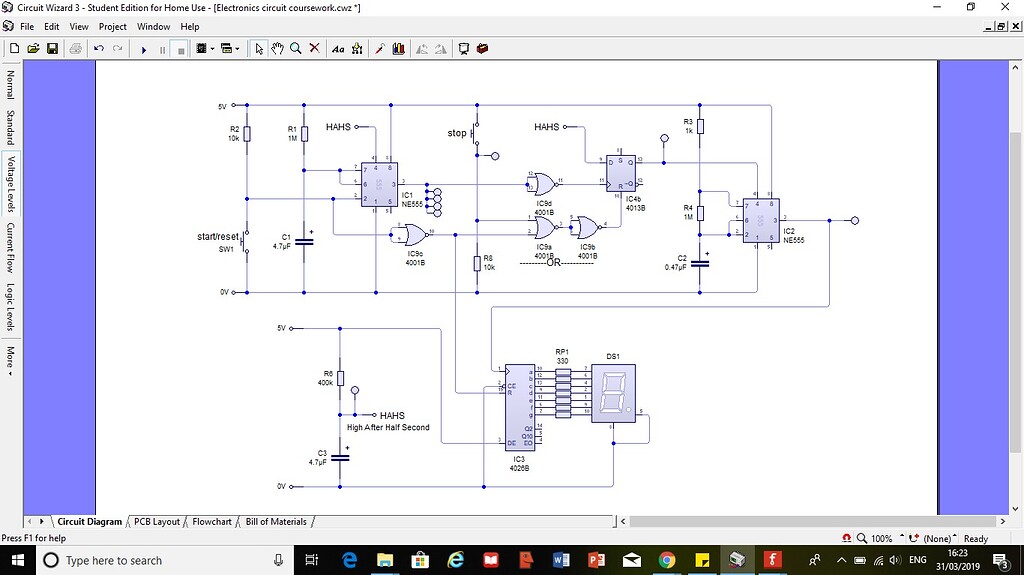
7 Computer aided design and specialist drawing programs
Computer aided design or CAD can be used in a number of different ways such as:
- CAD freehand sketching
- 2D modelling
- 3D modelling
- System design
- Often used to design items to be made using computer aided manufacture (CAM) - like a lasercutter or 3D printer.

8 Record and justify design ideas clearly - annotated sketches
- Annotation can be used with all of the above techniques.
- They help to explain the ideas without the need to speak to them directly.
- The can vary depending on what stage of the design process they are being used.
Design justifications:
- user and design requirements
- pros and cons of each design
- ergonomics
- sustainability considerations
Manufacturing details:
- materials and components
- dimensions
- manufacturing process and techniques
- sources of energy e.g. batteries, main, solar, wind etc.
9 Summary
- Decide on suitable design strategies for your design problem or scenario
- Choose a range of suitable communication techniques for your design problem or scenario.
10 Exam questions
- Explain one reason why annotations are important when a designer passes their concepts to a manufacturer.
- Explain one benefit and one drawback of freehand sketching versus CAD modelling.
- Name two different design strategies that designers sometimes use.
- List five things that a designer might annotate on their designs.
- Choose a suitable communication technique and sketch out a product that you might find in your design engineering workshop.
- Consider the advantages and disadvantages of collaborative designing.
- Discuss the potential differences in communication techniques for the following products: pop up children's book, interior of a wedding venue, clothing for a triathlon athlete and systems for an Amazon locker