| Design Engineering Theory Topics - Home Page |
Papers and Boards
1 Key terms
Paper
- A thin flat material made from natural fibres weighing less than 220 gsm.
Board
- Board is thicker than paper or layers of paper more than 220gsm.
2 Paper
- Paper is a thin material produced by pressing together moist fibres of cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets. It is a versatile material with many uses, including writing, printing, packaging, cleaning, and a number of industrial and construction processes.
- In Europe, paper and board is measured in grams per square metre (gsm).
- This means the number of grams a 1m X 1m sheet weighs 80-220gsm.
- There is a suggestion that the thicker the paper, the better the quality.
- Standard copier paper is usualy 80gsm. with typical writing paper being 120gsm.
Copier Paper
- Weight - 80gsm.
- Description - Thin, lightweight, cheap, bright white paper, with a smooth, bleached, uncoated surface.
- Uses - Writing, printing and drawing.
- Advantages - Takes colour well, good surface for pencils, pens and markers, cheap, readily available and in a range of colours.
- Disadvantages - Can be prone to jamming printer feed mechanisims.
Cartridge Paper
- Weight - 120-150gsm.
- Description - Creamy, thick heavyweight paper.
- Uses - General drawing and printing, can be used with watercolour paints without buckling.
- Advantages - Accepts most drawing media, opaque.
- Disadvantages - Costs more than copier paper.
Tracing Paper
- Weight - 60-90gsm.
- Description - Thin, smooth and translucent, made by beating to remove air and processing to make a dense, strong paper.
- Uses - Art, making copies, envelop windows and overlays on working drawings.
- Advantages - Strong, translucent.
- Disadvantages - Can be expensive, limited ink absorption and longer drying time.
3 Boards
- Paperboard is a thick paper-based material. While there is no rigid differentiation between paper and paperboard, paperboard is generally thicker (usually over 0.30 mm, 0.012 in, or 12 points) than paper.
- According to ISO standards, paperboard is a paper with a grammage above 250 g/m2, but there are exceptions.
- Paperboard can be single- or multi-ply. Paperboard can be easily cut and formed, is lightweight, and because it is strong, is used in packaging.
- Another end-use would be graphic printing, such as book and magazine covers or postcards. Sometimes it is referred to as cardboard, which is a generic, lay term used to refer to any heavy paper pulp–based board.
- Paperboard is also used in fine arts for creating sculptures.
Folding boxboard

- Description - Stiff layers consisting of:
- A printable bleached virgin pulp top surface.
- Unbleached yellowish centre layers.
- A bleached inside layer.
- Uses - Cereal boxes, food and health packaging and cartons.
- Advantages -
- Excellent for scoring and bending without splitting.
- Accepts print well.
- Inexpensive.
- Disadvantages -
- Lower strength than solid white board.
Corrugted board
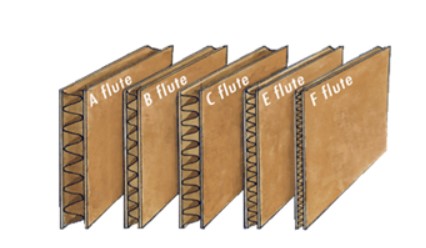
- Description -
- Two or more layers of fluted paper sandwiched between to paper liners.
- Available in different thicknesses.
- Strong and lightweight.
- Uses - Protective packaging, for example boxes for electrical products and CD sleeves.
- Advantages - Impact resistant, inexpensive, recyclable.
- Disadvantages -
- Brown finish does not convey quality.
- Can deform under pressure.
- Not water resistant.
Solid White Board

- Description -
- Strong, rigid board made from pure, bleached wood pulp.
- Excellent printing surface.
- Uses - Book covers, food, cosmetics and medicine packaging.
- Advantages - Strong, rigid and accepts print well.
- Disadvantages - Can be expensive.
4 Properties
Flexibility
- Amount of material bends when a force is applied (stiffness), determined by its thickness and weight.
- Flexural stiffness is resistance to an external bending force.
- Handling stiffness is the ability to support its own weight.
Printability
- Ability to accept a printed image onto its surface (porosity).
- Affected by surface properties, such as smoothness or finish, and structural properties, such as bulk or thickness.
- Not the same as print quality, which is determined by other factors such as alignment of plates on the machinery.
Biodegradability
- Ability to be broken down by bacteria or other biological means.
- Most uncoated paper products are biodegradable because they are made from wood pulp.
- Compostable means that a material can biodegrade in less than 12 weeks.
5 Sample questions
- Paper and card are extremely useful materials that are processed from wood fibres. They come in many different sizes and forms.
- How many paper products have you used today?
- Why do you think that some boards are laminated with other materials, such as foil.
- How many different paper sizes do you know (list 3).
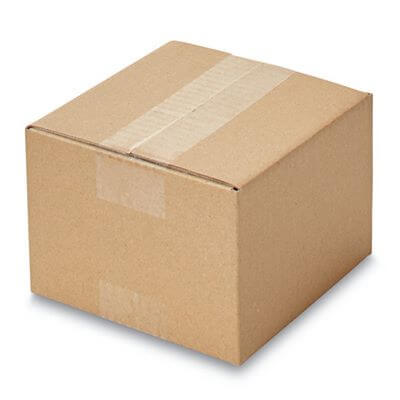

- The box in the image above is used to package CDs sent to a supermarket.
- Explain one reason why this material is suitable for the box. (2)
- Explain one disadvantage of this material. (2)
- Name three different paper types.
- State an advantage of using folding boxboard.
- Explain why printing might affect the quality of a finished product?
- Describe and compare the properties of two different boards. Evaluate which one would be best for a new perfume package?