| Week 1 | Week 2 | Week 3 | Week 4 | Week 5 | Week 6 | Homework Tasks |
An Introduction to Mechanisms
1 Gears
Learn It
- Gears work a little like pulleys without the need for a belt. The two rotating parts have teeth that mesh together passing the motion from one gear to the next.
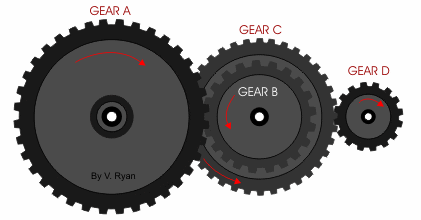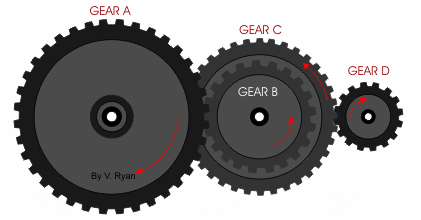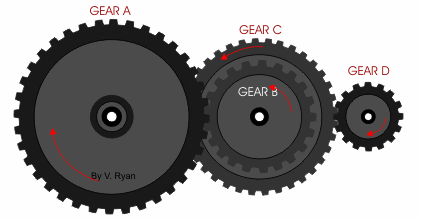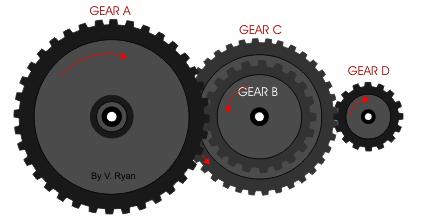
- We can use gears to change:
- The direction of motion
- The speed
- The advantage of a gear over a pulley is the meshing prevents slippage so greater forces can be applied.
Learn It - Gear calculation
- Velocity ratio = number of teeth on the driven gear / number of the teeth on the driver gear = input speed / output speed
Output speed = input speed / ratio
Here is a worked example:

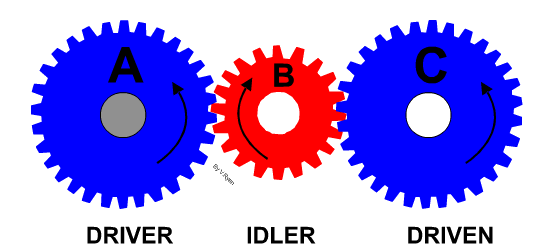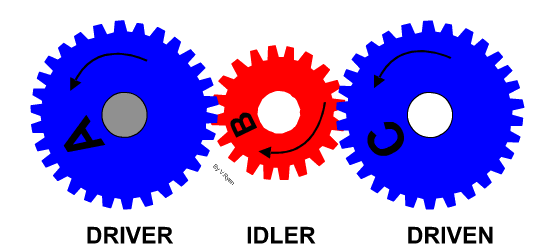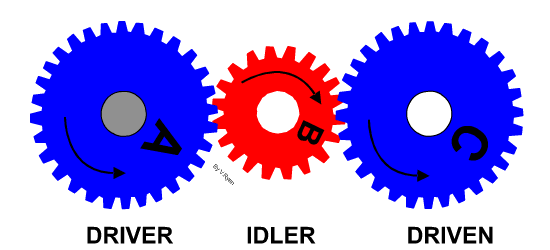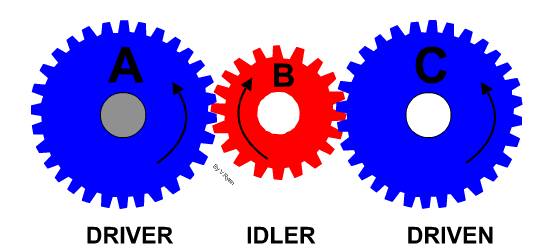
Learn It - Idle gears
- An idle gear is used to change the direction of the output/driven gear or used to connect gears where a large centre distance is needed.
- They do not change the speed ratio.
Badge It - Silver
Using a word processor and calculator answer the following questions:
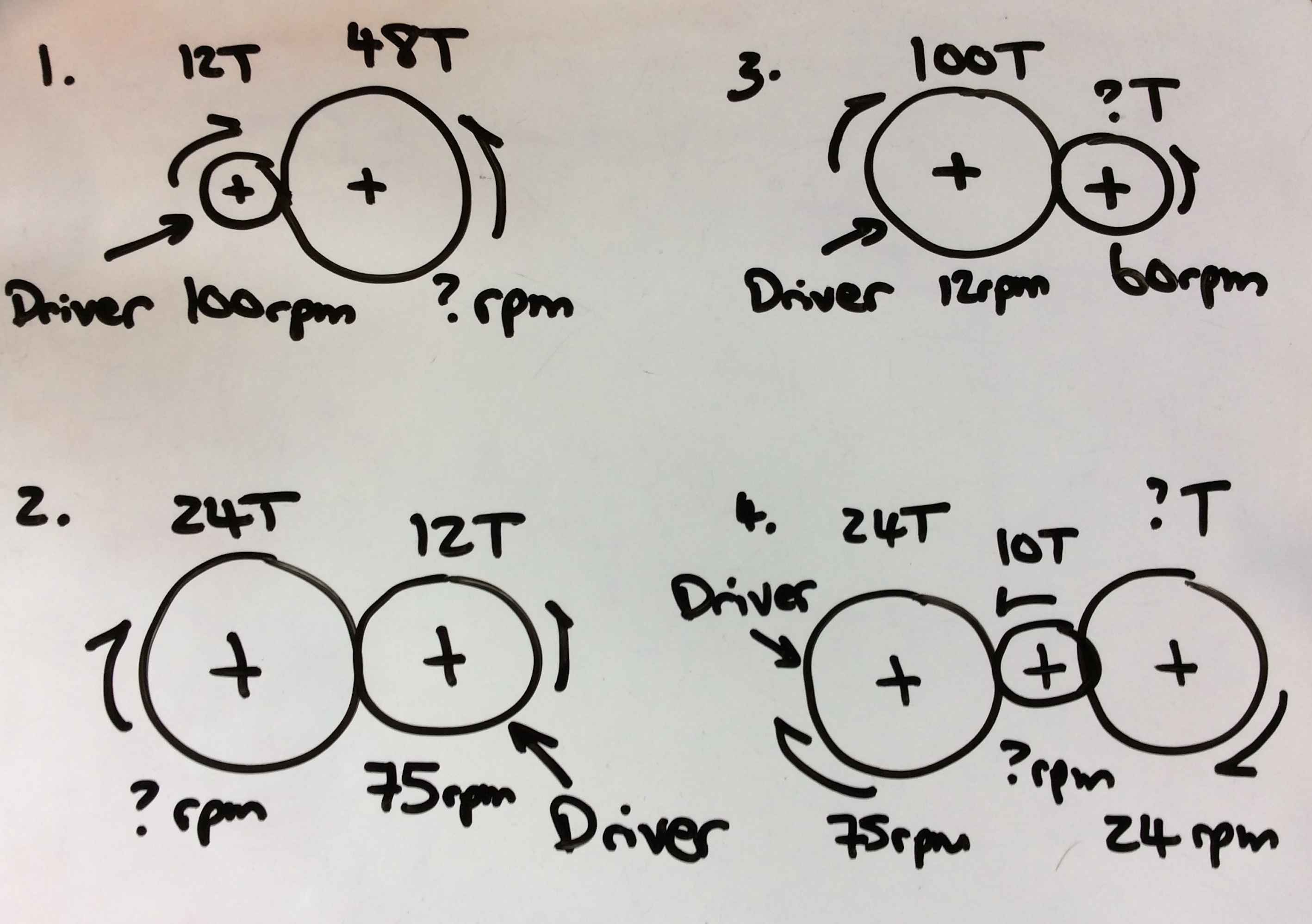
To get the badge upload your calculations and then complete the quiz here.
Badge It - Gold
- Using a Wakano set build and photograph the following gear trains:
- 1:3 ratio
- 1:2 ratio
- 1:1 same direction
Photograph all three at the same time for the gold badge.
Learn It - Gear trains
- Gear trains, two or more gear joined together, can be simple or compound.
- The difference Compound gear trains have more than one gear on a shaft.
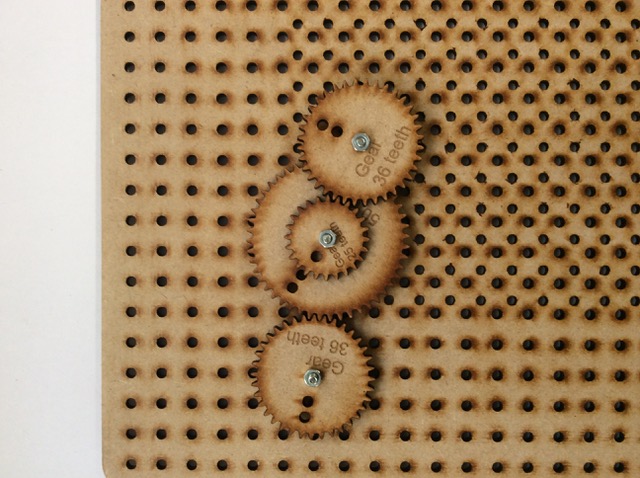

Badge It - Platinum
- Build a compound gear train.
- Research and report on bevel gears and rack and pinion.
- Your report should include an image of your compound gear train and an explanation of how, (bevel and rack and pinion) they work, and examples of their use, including diagrams.
Learn It - Advanced mechanisms
- As an extension task try and build any/all of the following four mechanisms:
- Crank and slider
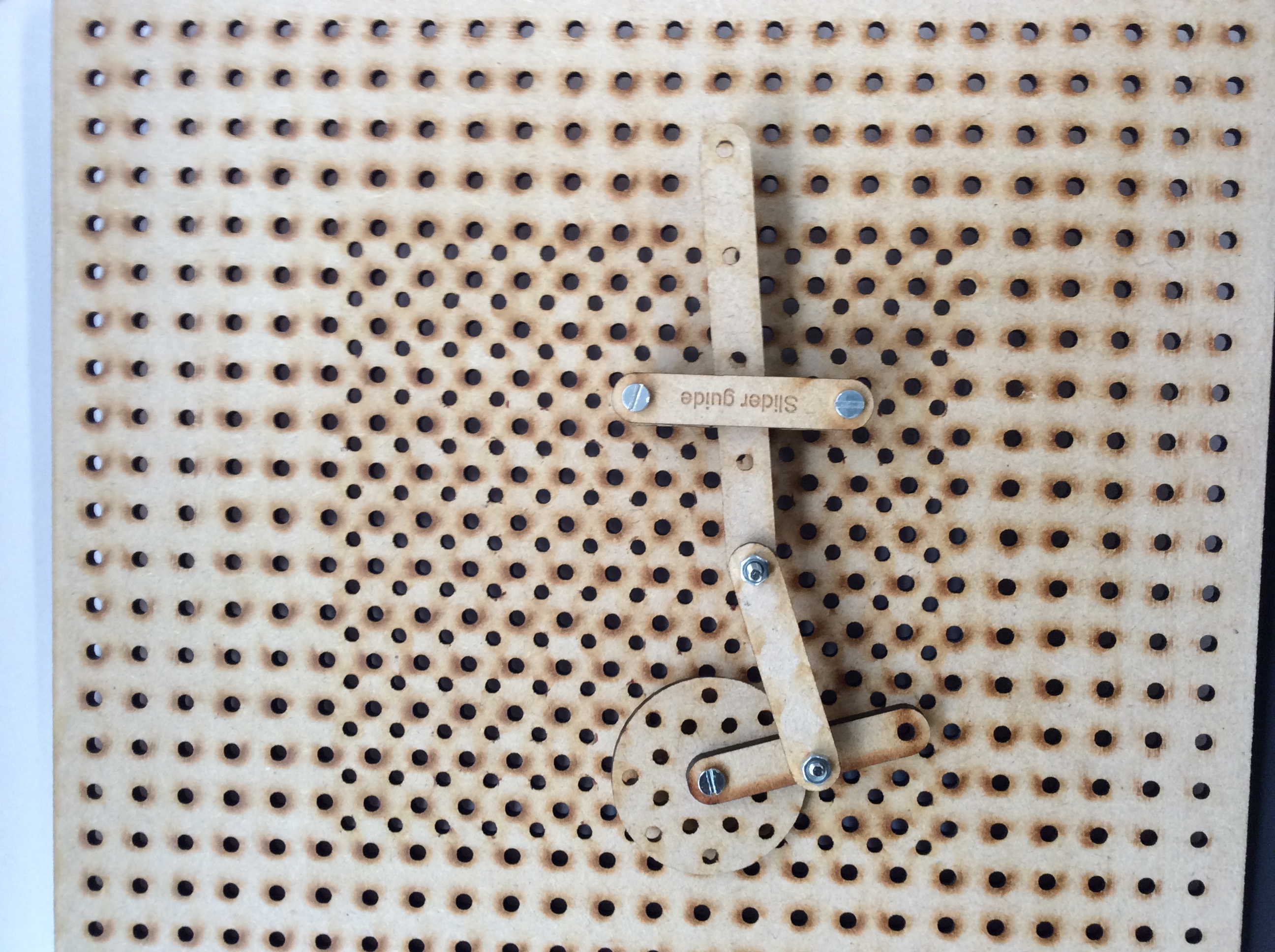
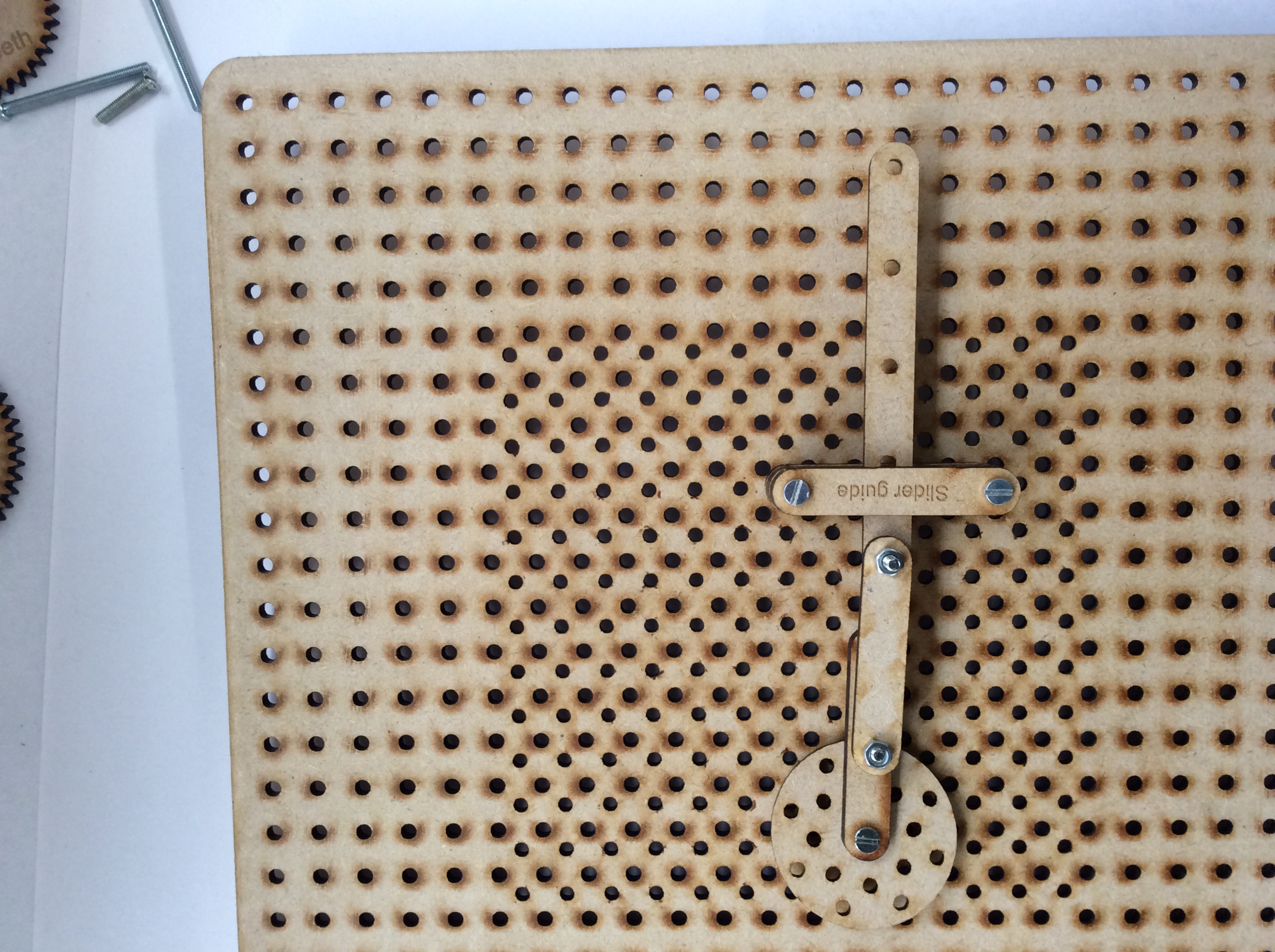
- Peg and slot
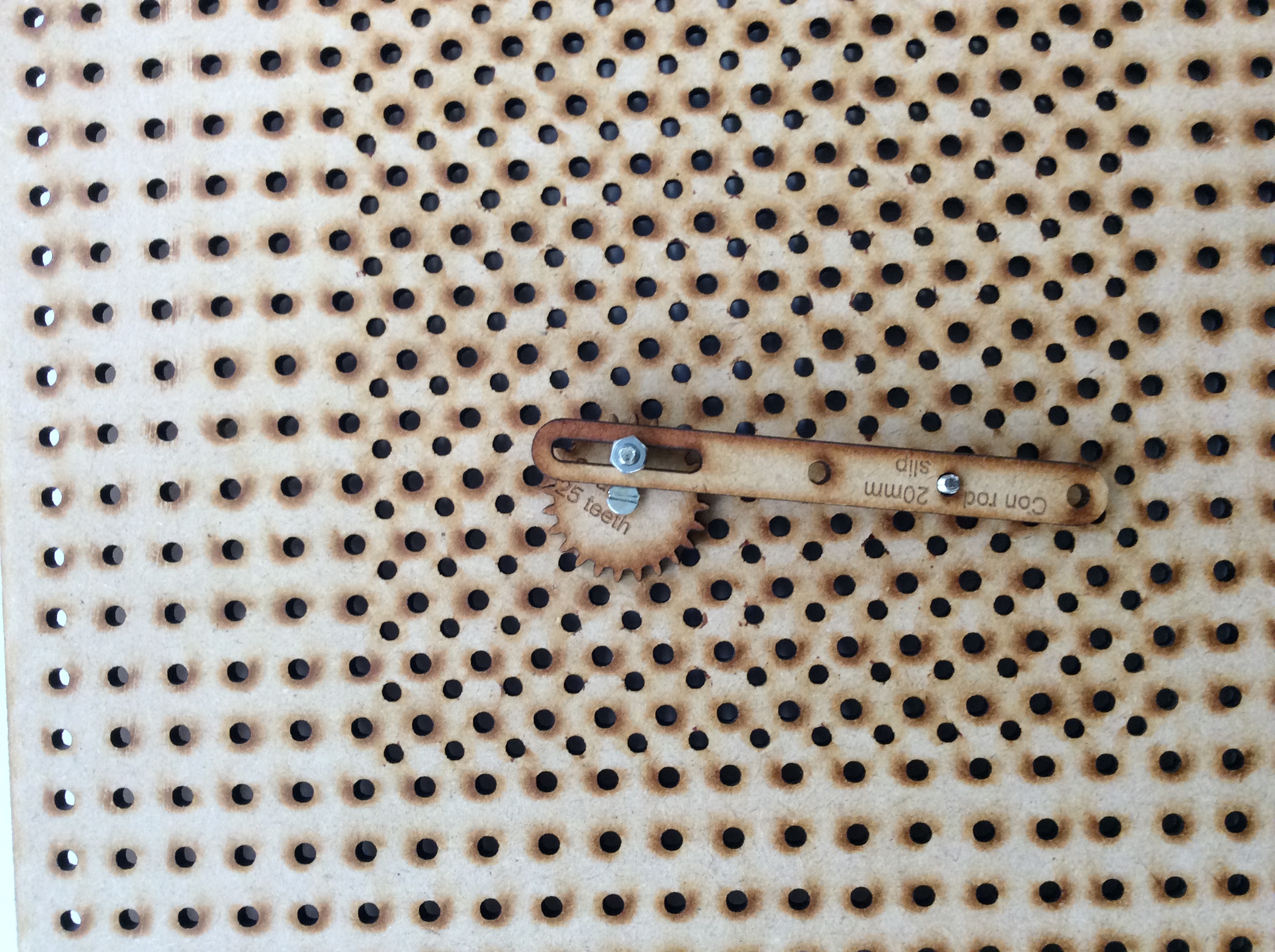
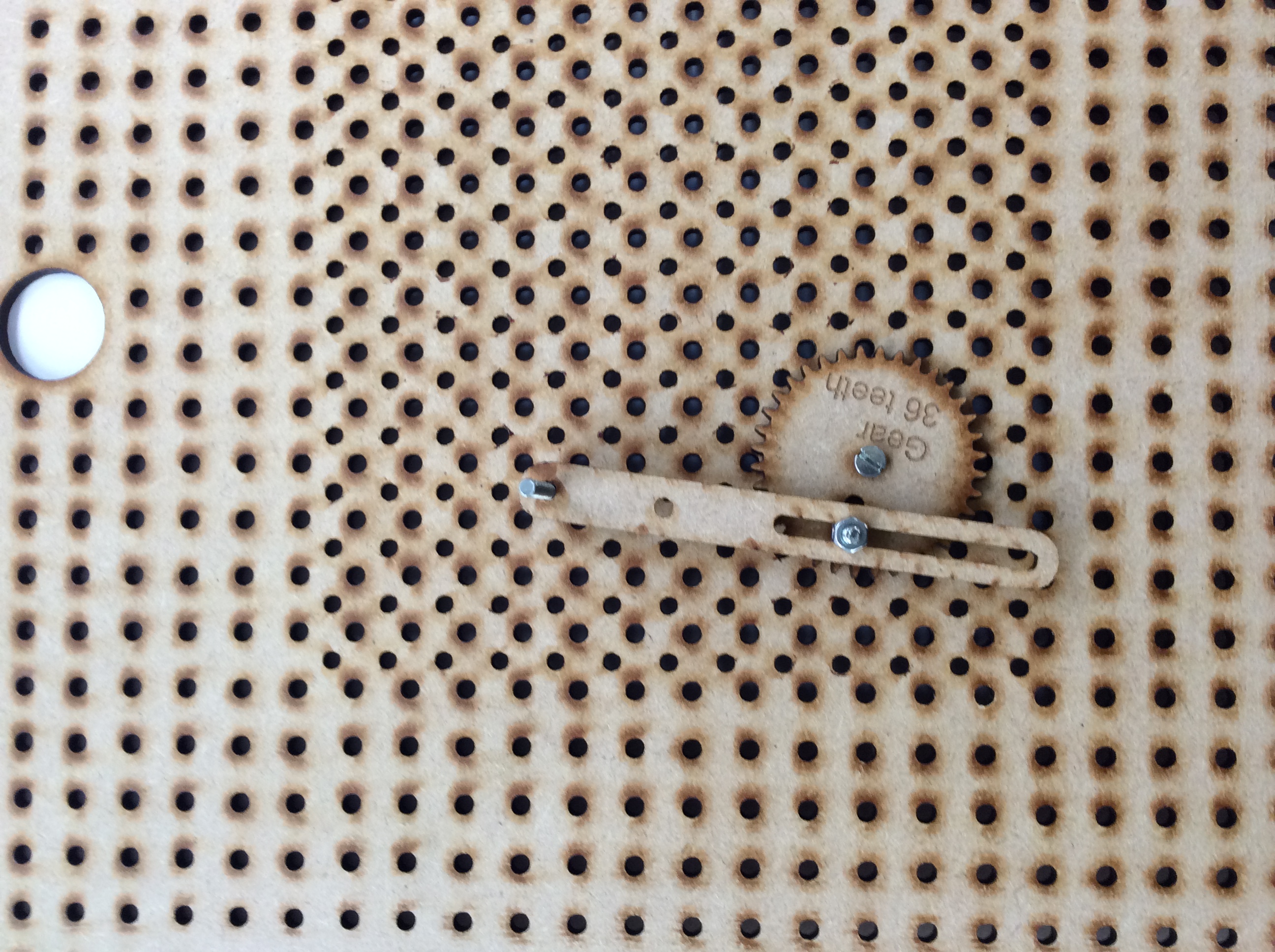
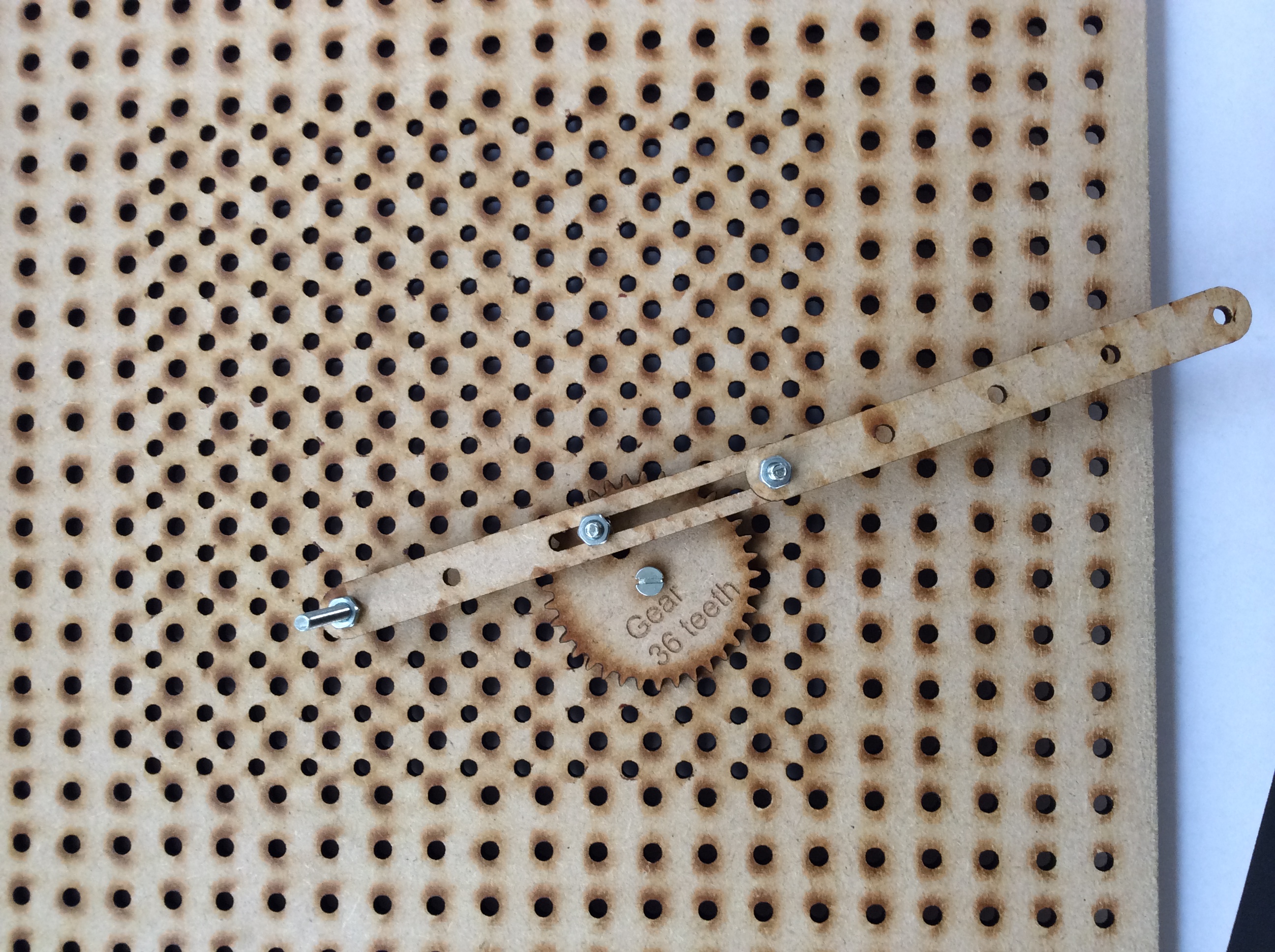
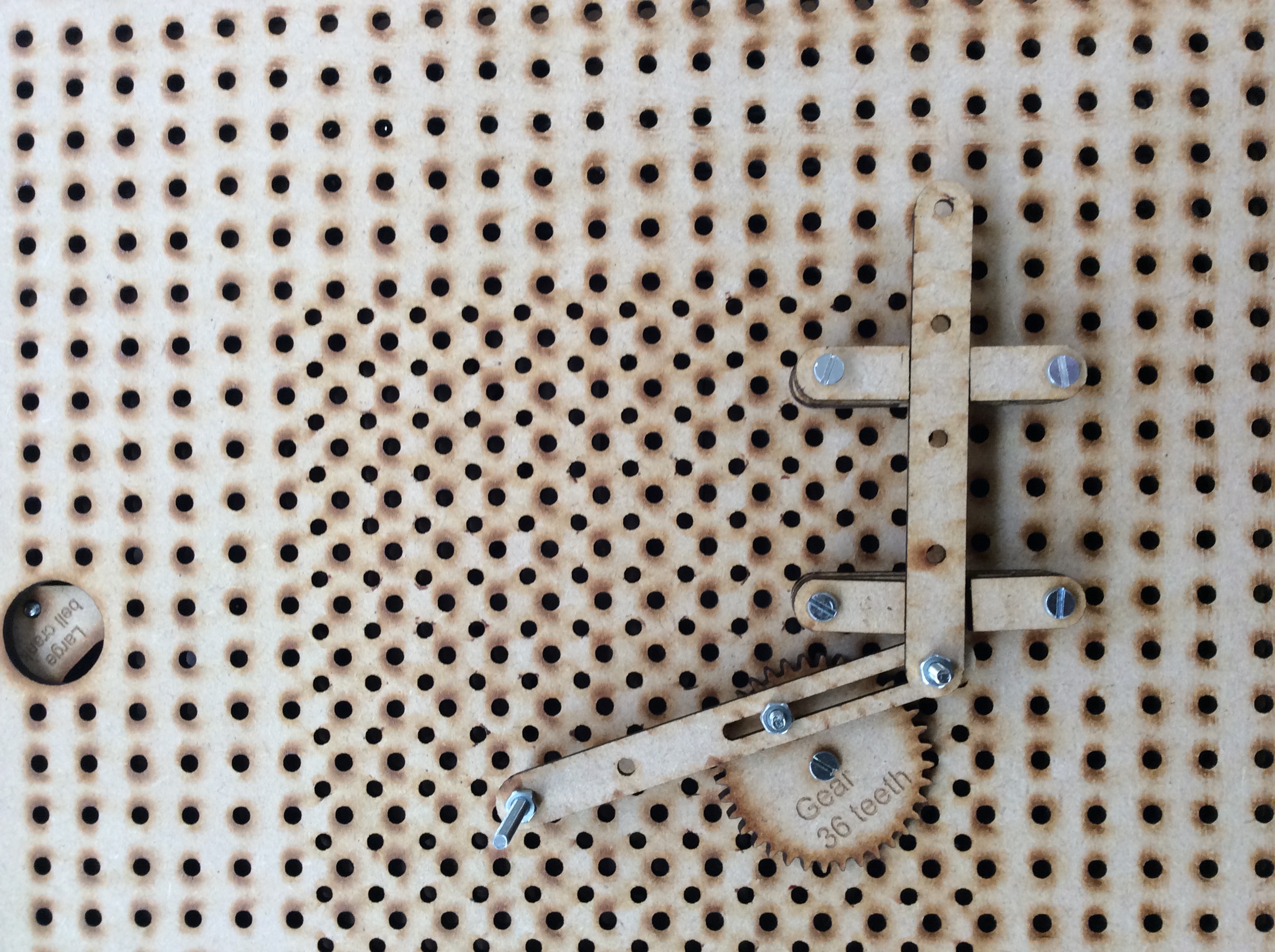
- Peg slot and slider
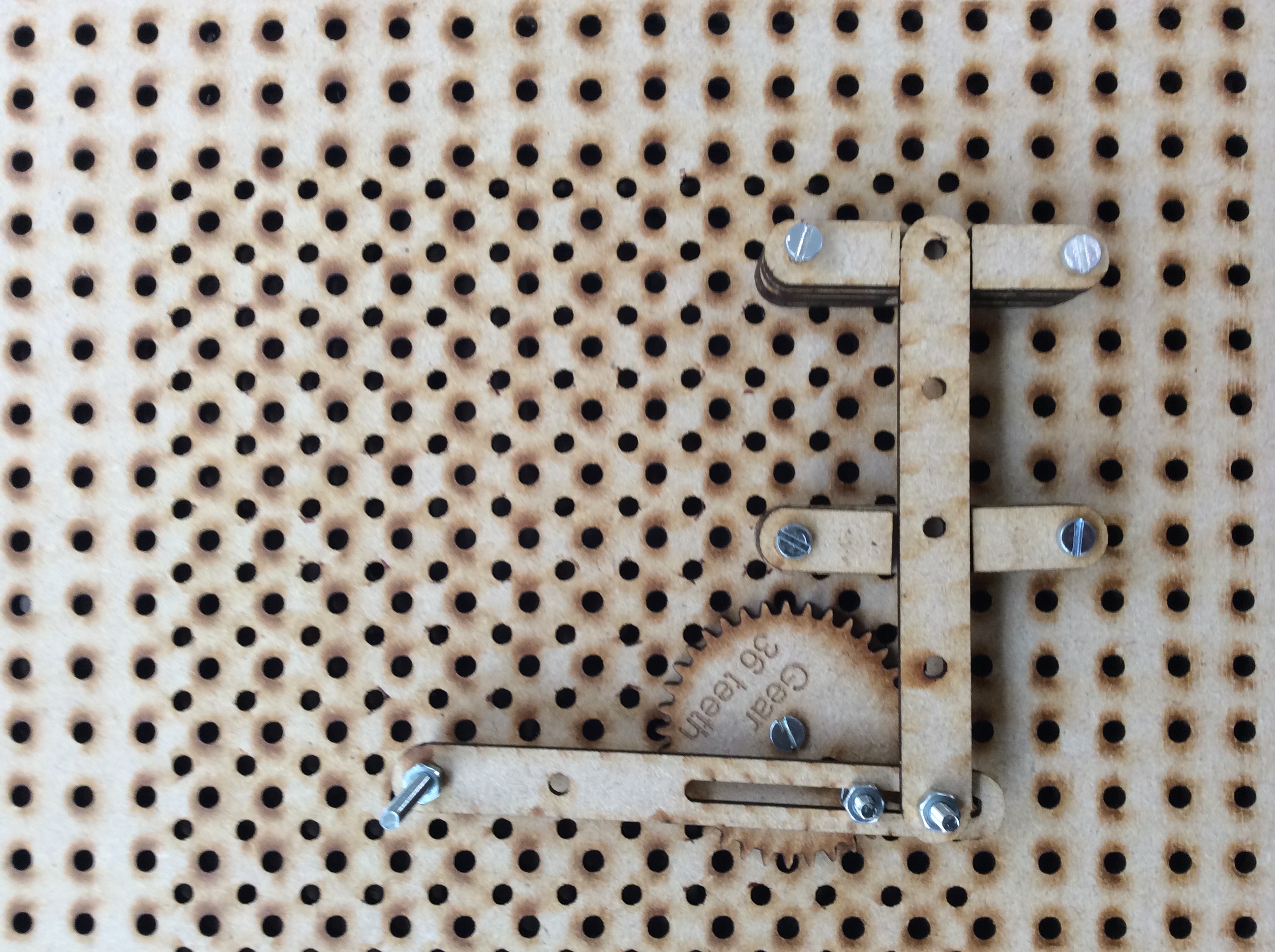

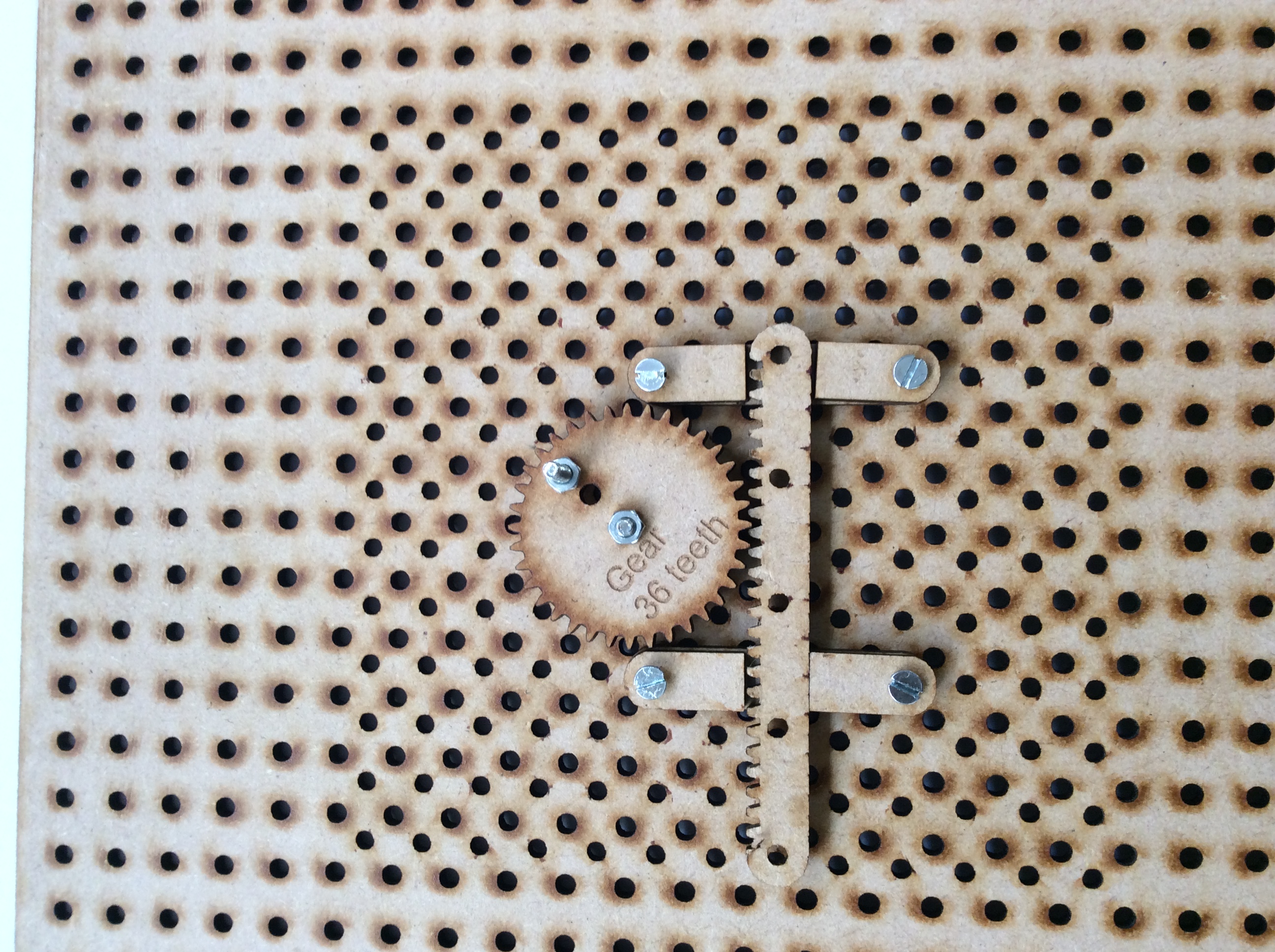
- Rack and pinion
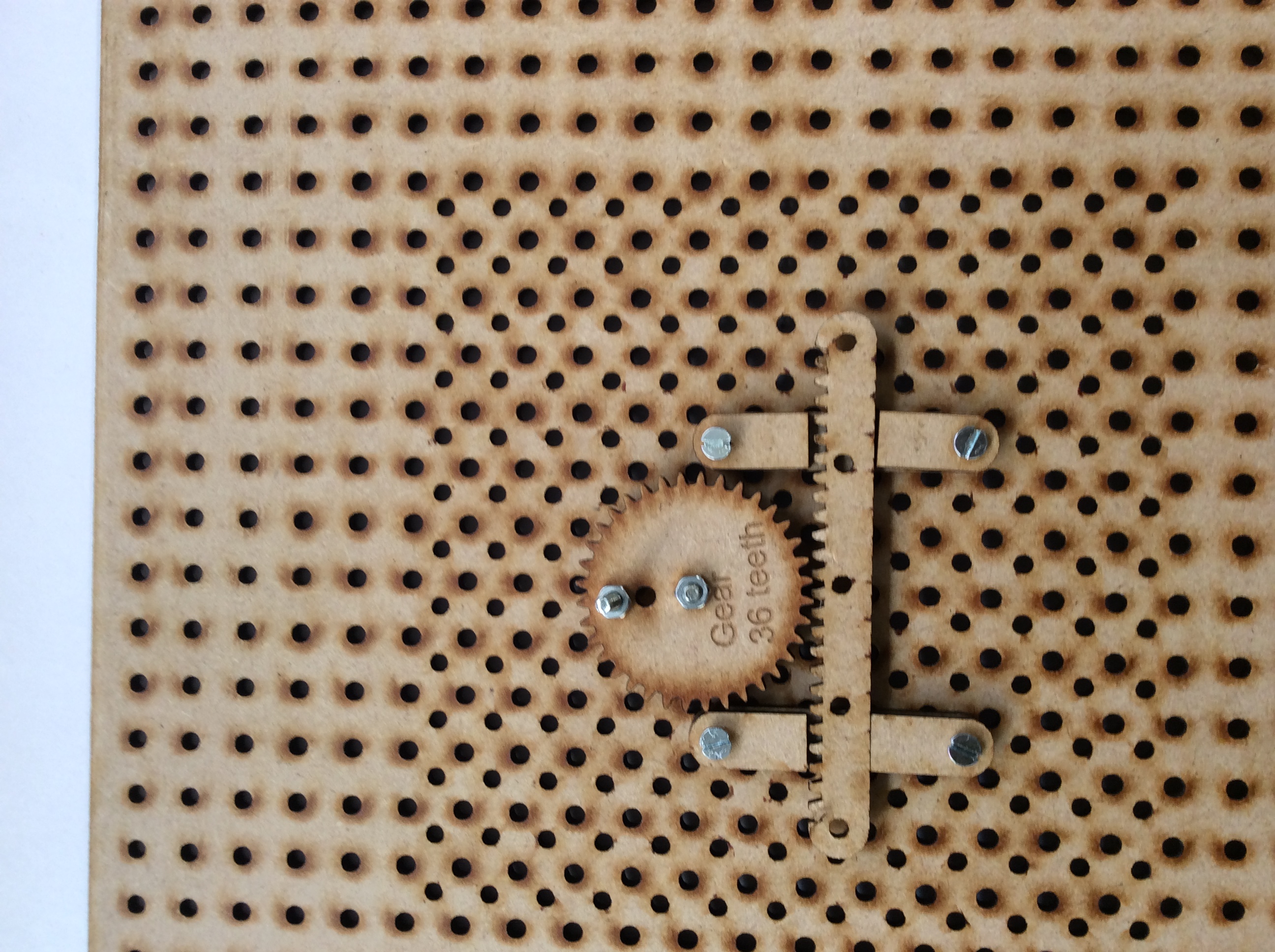

Extension for Solidworks
Spur gear - Click here for the video
Rack and pinion - click here for the video
Bevel gear - click here for the video