| Design Engineering Theory Topics - Home Page |
Electronic Systems
1 Introduction
- This is a very basic introduction into core electronics for all DT students. We are going to cover all of these and more in our specified specialised topic Systems.
- Electronic systems can have one or many inputs and outputs and a controller between them.
- The system read in the input signals and controls the the output signals according to the instructions in the program it has been given.
INPUT DEVICE > CONTROL > OUTPUT DEVICE
- Here is an example of a systems diagram from a very good website www.technologystudent.com, please have a look at the resources.
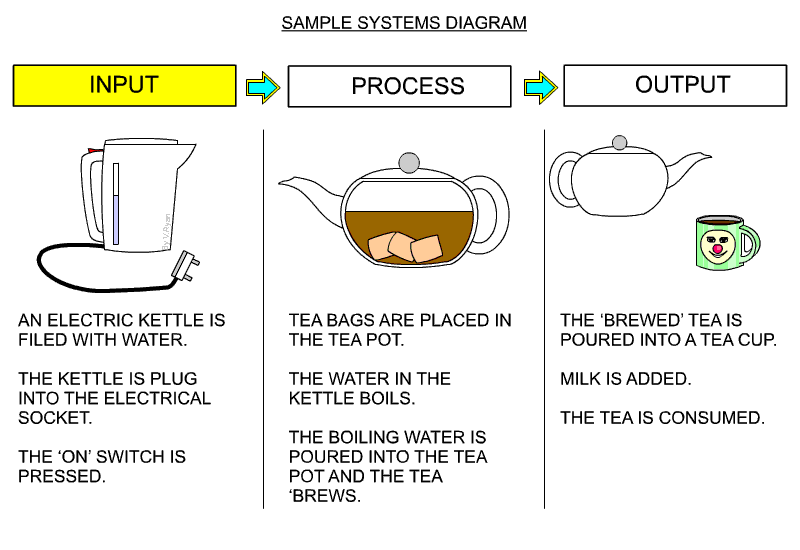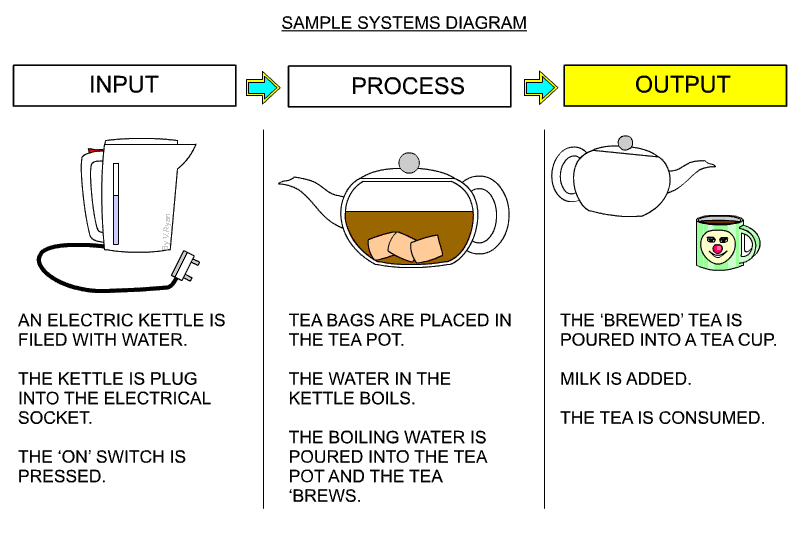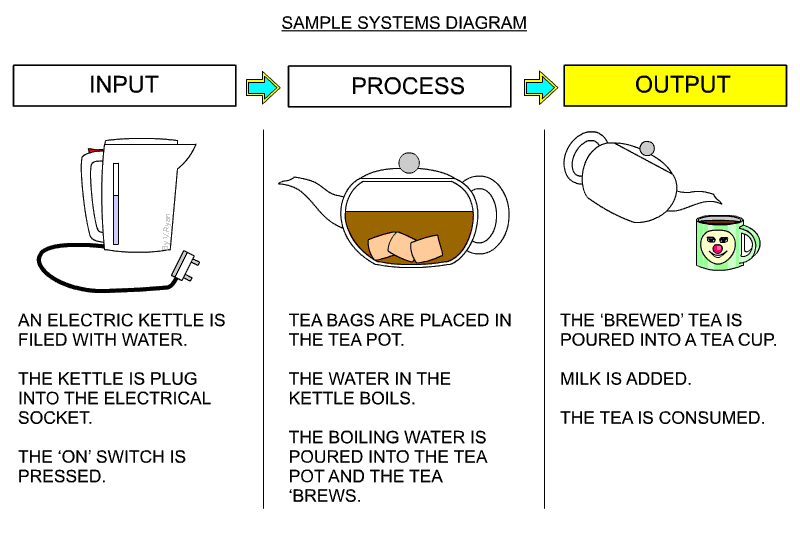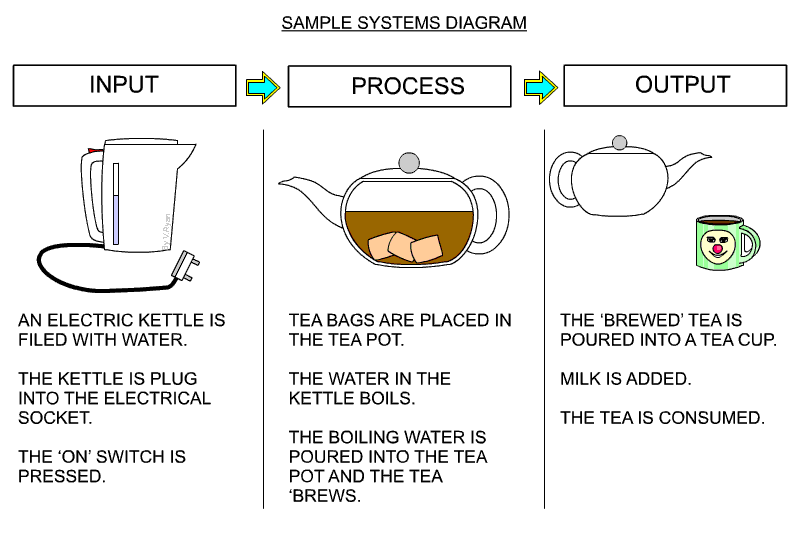
2 Sensors
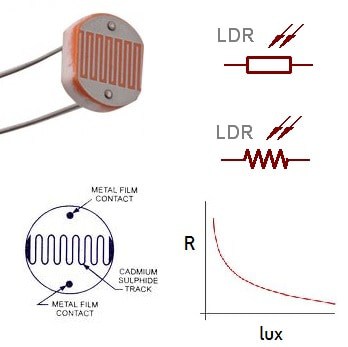
Light dependent resistor(LDR)
- When the light falls on the sensor its resistance changes:
- in the light the resistance is low so the electrons flow
- in the dark the resistance is high so not much electricity flows.
Thermistor
- is a temperature dependent resistor.
- Its resistance changes with temperature
- in the warm, the resistance is low
- in the cold, the resistance is high
3 Control component and devices
- As well as sensors there other components that can provide input into a circuit.
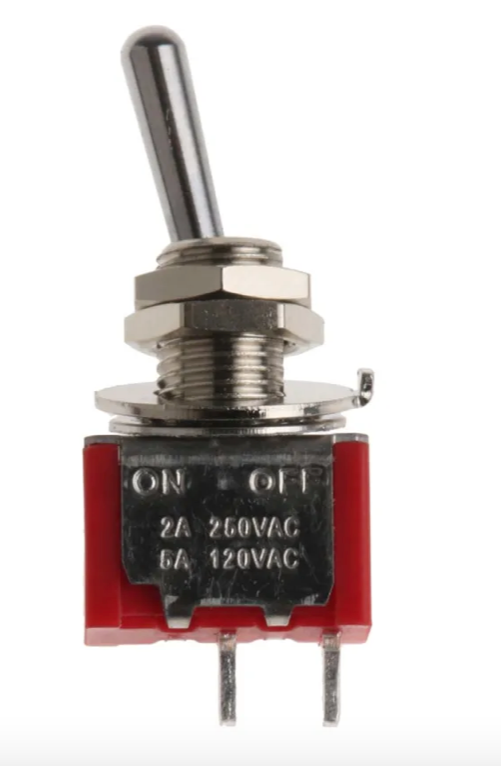
Single Throw Switch
- This is an on and off switch for simply controlling the circuit to be on or off.

Resistors
- this component changes the resistance of a circuit.
- It limits the flow of the electrons.
- This maybe to protect delicate components e.g. LEDs or to help control the flow of electricity around a circuit such as using a pull down resistor.
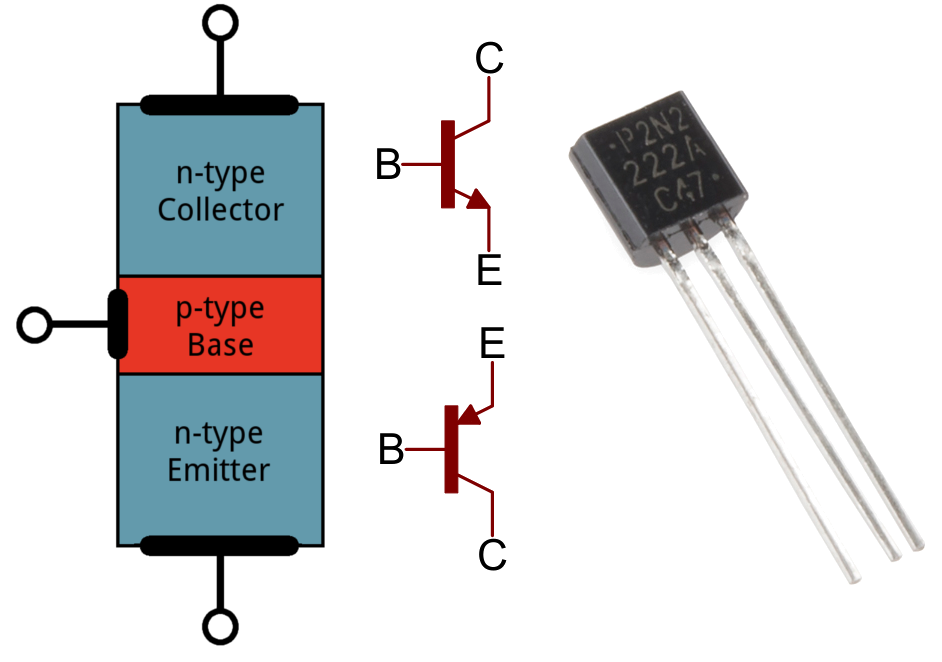
Transistors
- acts like a tiny electronic switch.
- They have three legs - base, collector and emitter.
- The are made from a semi-conductor and the base acts as a gate controlling the flow from the emitter to the collector.
- They are useful in sensing circuits to amplify the small current you get from some sensors.
- They can be extremely small by etching them into silicon wafers known as silicon chips. A mobile phone may contain 2 billion transistor.
4 Outputs
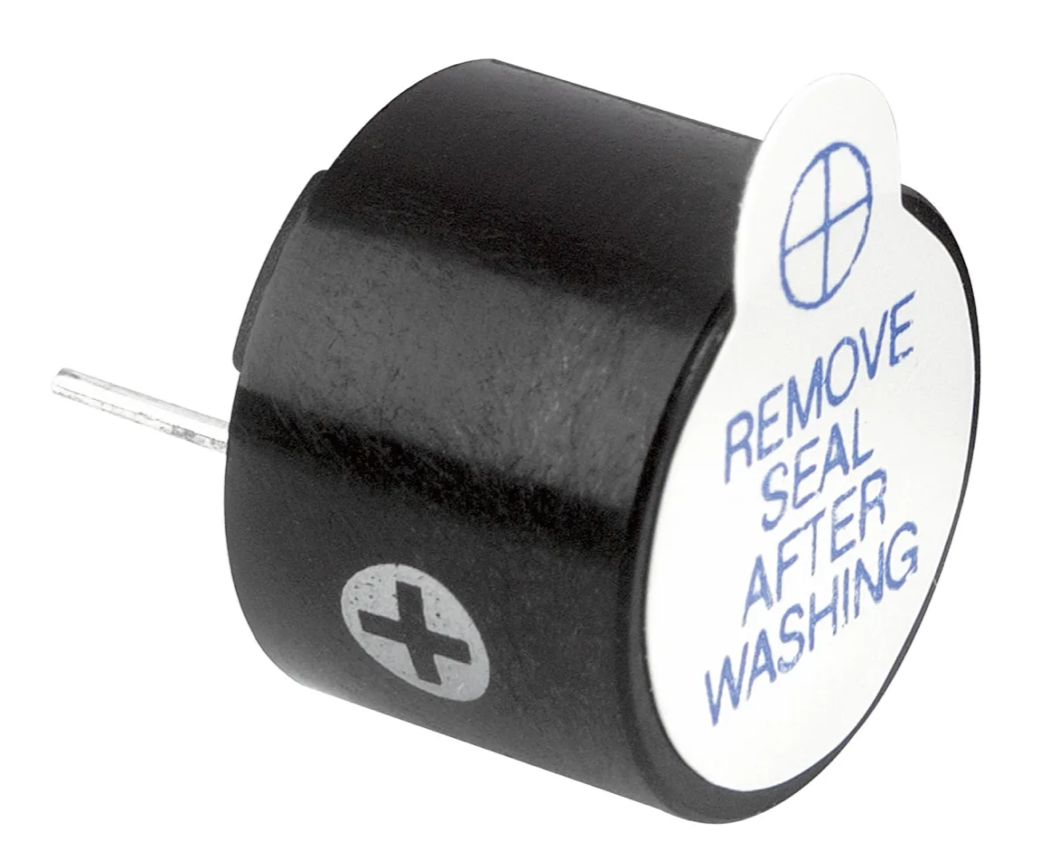
Buzzer
- A buzzer is an audio device than can be useful as a warning sound.

Light-emitting diode(LED)
- This gives out light when electricity is passed through, in a range of colours, that can be powerful to light a whole room.

5 Definition
Input device
- Something that can give an input signal to the system.
Output device
- Something that can responses to an instruction to change from the control system.
Input signal
- Information give to the system from an input device.
Output signal
- An instruction the system gives to an output device.
Program
- A set of instructions the system controller has been given to make the electronic system do what it is supposed to do.
- A transistor can bypass the need for a program as a simple switching action happens due to the rise in voltage on the base of the transistor above 0.6 Volts.
Resistance
- An electrical quantity that is a measure of how the device or wire reduces the electric current flow through it.
Component
- An individual part of a circuit
Circuit
- Individual parts are joined together with a conductive material so electricity can flow through them and perform a task.
Voltage
- The amount of potential electrical force available that could make electricity flow.
- Click on this link to see the effects on Voltage and Current
Current
- The amount of electricity that is flowing through a circuit.
- Click on this link to see the effects on Voltage and Current
Semi-conductor
- A material that allows electricity to flow under certain conditions. It can behave as an insulator or conductor.
- To learn more about semi-conductors, click on this link.
Exam Style Questions
- What are the 3 main components of an electronic system?
- Name 2 possible input devices?
- Name 2 possible output devices?
Challenge
- Draw a block diagram for a computer, showing some of its input devices and output devices.
- Find out the units of resistance and explain how resistance is marked on a resistor.
Extended information
